akak nak boh nasihat2 plak dalam blog ni
tak tau nak boh apa dah
belasah je la ye apa akak nak boh
kik3
mari kita bincang kan ..
10 Common Reasons Most People Fail
1. They don’t look before they leap.
keje2 spontan ni memang baguih, cuma kena plan elok2. contoh nya kalau nak pi intibiu tu kan.. study la dulu bebanyak pasai company tu, pasai ethic masa intibiu, macam2 lah..
2. They don’t want it enough.
ni macam nak taknak je, kalau nak betol2 mesti workout to it. alahhhh macam nak slim lahhh, agak2 dah 10 tahun tak slim2 tu, ko btol2 nak slim ke sebenar nya?? kik3 terkena akak deknonnn.
3. They don’t look for alternatives.
plan B kena ada gak deknon. kot2 plan A idak menjadik kann. contoh nak beli gelang emas sampai 40g, tapi duit tak cukup. plan B nya? beli la gelang 20g jek, yang cukup2 duit tu laaa.. tapi still ko dpt gelang mas gak kan??
point2 di bawah tak perlu penerangan la kan?
4. They give up.
5. They don’t have a goal.
6. They don’t seek advice from others.
7. They listen to too much advice.
point 6 n 7 nih related kan?
ye laa tak carik penasihat pun salah
terover dengar nasihat pun salah deknonnn
jadi pilih yang sedang2 aje ye??
juga point2 di bawah ni pun perlu untuk kita berjaya:
8. They have too many excuses.
10. They misjudge.
Wednesday, May 28, 2014
Tuesday, May 27, 2014
Basic Account: Chapter 3: Accounting Cycle.
The Accounting Concept
===================
Accounting Period Concept: When accountants prepare financial statements, they assume that the economic life of the business can be divided into the time periods.
Cash Basis: Revenues and expenses are reported in the income statement in the period in which cash is received or paid.
Accrual Basis: Revenues are reported in the income statement in the period in which they are earned.
Revenue Recognition Concept: Revenues are reported when the services are provided to customer and cash may or may not be received.
Matching Concept : The accounting concept that supports reporting revenues and related expenses.
Nature of Adjusting Process
=====================
Adjusting Entries: The journal entries that bring the accounts up to date at the end of accounting period. Adjusting entries will always involve a revenue or an expense account and an asset or liability account.
Prepaid Expenses: Or deferred expenses, are items that have been initially recorded as assets but are expected to become expenses over time or through the normal operation of the business.
Unearned Revenue: Or deferred revenues, are items that have been initially recorded as liabilities but are expected to become revenues over time or through the normal operations of the business.
Accrued Revenues: Or accrued assets, are revenues that have been initially incurred but have not been recorded in the accounts.
Accrued Expenses: Or accrued liabilities, are expenses that have been initially incurred but have not been recorded in the accounts.
Financial Statements
=================
Income statement: Is prepared directly from the adjusted trial balance.
Statement of Owner's Equity: Is the balance of the owner's capital account.
Balance sheet: Assets, liabilities and owner's equity are presented.
Assets: Commonly divided into classes for presentation which are:
1. current assets
2. fixed assets.
Liabilities: Two common classes of liabilities are:
1. current liabilities
2. long-term liabilities
Owners equity: The owner's right to the assets of the business
Adjusting and Closing Entries
========================
Real Accounts: Relatively permanent, carried forward from year to year.
Temporary Accounts: Or nominal accounts, accounts report amounts for only one period and not carried forward from year to year; account incomes, account expenses and account withdrawals.
Closing Process: Entries that transfer the balance of temporary accounts to the owner;s equity.
===================
Accounting Period Concept: When accountants prepare financial statements, they assume that the economic life of the business can be divided into the time periods.
Cash Basis: Revenues and expenses are reported in the income statement in the period in which cash is received or paid.
Accrual Basis: Revenues are reported in the income statement in the period in which they are earned.
Revenue Recognition Concept: Revenues are reported when the services are provided to customer and cash may or may not be received.
Matching Concept : The accounting concept that supports reporting revenues and related expenses.
Nature of Adjusting Process
=====================
Adjusting Entries: The journal entries that bring the accounts up to date at the end of accounting period. Adjusting entries will always involve a revenue or an expense account and an asset or liability account.
Prepaid Expenses: Or deferred expenses, are items that have been initially recorded as assets but are expected to become expenses over time or through the normal operation of the business.
Unearned Revenue: Or deferred revenues, are items that have been initially recorded as liabilities but are expected to become revenues over time or through the normal operations of the business.
Accrued Revenues: Or accrued assets, are revenues that have been initially incurred but have not been recorded in the accounts.
Accrued Expenses: Or accrued liabilities, are expenses that have been initially incurred but have not been recorded in the accounts.
Financial Statements
=================
Income statement: Is prepared directly from the adjusted trial balance.
Statement of Owner's Equity: Is the balance of the owner's capital account.
Balance sheet: Assets, liabilities and owner's equity are presented.
Assets: Commonly divided into classes for presentation which are:
1. current assets
2. fixed assets.
Liabilities: Two common classes of liabilities are:
1. current liabilities
2. long-term liabilities
Owners equity: The owner's right to the assets of the business
Adjusting and Closing Entries
========================
Real Accounts: Relatively permanent, carried forward from year to year.
Temporary Accounts: Or nominal accounts, accounts report amounts for only one period and not carried forward from year to year; account incomes, account expenses and account withdrawals.
Closing Process: Entries that transfer the balance of temporary accounts to the owner;s equity.
Monday, May 26, 2014
Basic Accounting: Chapter 2: Analyzing Transactions
An accounting system is designed to show the increases and decreases in accounts in the financial statements.
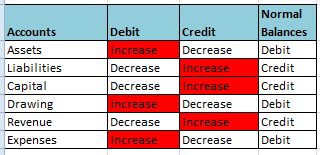
5 major types of accounts in financial statements:
1. Assets
2. Liabilities
3. Owner's Equity
- Capital
- Drawing
4. Revenue
5. Expenses
The rules of debit and credit apply to these accounts:
Recording Process
==============
1. Journal
- Transaction takes place
- Determine whether an asset, a liability, owner's equity, revenue, or expenses is affected by a transaction
- Apply the rules of debit and credit
2. Ledger
- Periodically, the journal entries are transferred to the accounts in the ledger
- Ledger contains accounts that the company has; the list of accounts is normally known as chart of accounts.
3. Trial Balance
- The trial balance is a list of account balances from the ledger
- At the end of each accounting period, company will prepare a trial balance.
- The trial balance must balance, i.e. the total of the debit balances must equal to the total of credit balances.
Sunday, May 25, 2014
Basic Accounting: Chapter 1: Malaysian Accounting.
Types of Business
==============
1. Manufacturing business:
Changes raw materials (basic input) into finish goods that are sold to individual customers.
2. Merchandising business:
Purchases inventories from other businesses and resell these inventories to individual customers.
3. Service business:
Provides services instead of products to customers.
Accounting Professional Bodies
========================
FRF - Financial Reporting Foundation
Oversees MASB performance, financial and funding requirement and reviews proposed standard bu MASB.
MASB - Malaysian Accounting Standard Board
Adopt international accounting standards or develop new accounting standards for Malaysian companies.
MICPA - Malaysian Institution of Certified Public Accountant
To advance the theory and practice of accounting and to provide education, training and exam to accountants.
MIA - Malaysian Institute of Accountant
To develop, support and monitor quality and expertise consistent with global practice in accounting profession.
Accounting Information Users.
========================
Internal users:
Managers, employees who use financial information to make decisions.
External users:
Creditors, bankers, investors, government agencies and the general public who use financial inforamtion to support their decisions.
Accounting Assumptions
====================
1. Separate business entity: Accounting only records economic events which are related directly to a particular business.
2. Going concern: The assumption that businesses shall continue its operation to the foreseeable future.
3. Monetary unit: Business should report all the economics events in a monetary unit.
4. Time period: Business operation can be divided into specific period of time such as month, a quarter or a year.
Accounting Principles
====================
1. Historical cost principle: Business should report its activities as their actual cost.
2. Objectivity principle: Accounting records and reports should be base on objective evidence.
3. Revenue recognition principle: Revenue should be recognized as soon as i is earned and not in the period in which the business receives the cash.
4. Matching principle: Report the expenses in the period of which the revenue is actually earned as a result of these expenses.
5. Full disclosure principle: Require businesses ti disclose sufficient information to the users.
Accounting Constraints
==================
Conservatism: A concept to guide accountants to choose between available options. The selected option should minimize the possibility of overstating income or assets of the company.
Materiality: Require businesses to account only for the items that are deemed significant for a given size of operation.
Accounting Equation
=================
Asset = Liabilities + Owner Equity
Financial Statement Components
============================
Income statement: A summary of revenue and expenses for a specific period of time such as month or a year.
Statement of owners's equity: A summary of the changes in the owner's equity as of a specific date.
Balance Sheet: A list of assets, liabilities and owner's equity as of specific date, usually at the close of the last day of the month or a year.
Statement of cash flows: A summary of the cash receipts and cash payments for a specific period of time, such as a month or a year.
==============
1. Manufacturing business:
Changes raw materials (basic input) into finish goods that are sold to individual customers.
2. Merchandising business:
Purchases inventories from other businesses and resell these inventories to individual customers.
3. Service business:
Provides services instead of products to customers.
Accounting Professional Bodies
========================
FRF - Financial Reporting Foundation
Oversees MASB performance, financial and funding requirement and reviews proposed standard bu MASB.
MASB - Malaysian Accounting Standard Board
Adopt international accounting standards or develop new accounting standards for Malaysian companies.
MICPA - Malaysian Institution of Certified Public Accountant
To advance the theory and practice of accounting and to provide education, training and exam to accountants.
MIA - Malaysian Institute of Accountant
To develop, support and monitor quality and expertise consistent with global practice in accounting profession.
Accounting Information Users.
========================
Internal users:
Managers, employees who use financial information to make decisions.
External users:
Creditors, bankers, investors, government agencies and the general public who use financial inforamtion to support their decisions.
Accounting Assumptions
====================
1. Separate business entity: Accounting only records economic events which are related directly to a particular business.
2. Going concern: The assumption that businesses shall continue its operation to the foreseeable future.
3. Monetary unit: Business should report all the economics events in a monetary unit.
4. Time period: Business operation can be divided into specific period of time such as month, a quarter or a year.
Accounting Principles
====================
1. Historical cost principle: Business should report its activities as their actual cost.
2. Objectivity principle: Accounting records and reports should be base on objective evidence.
3. Revenue recognition principle: Revenue should be recognized as soon as i is earned and not in the period in which the business receives the cash.
4. Matching principle: Report the expenses in the period of which the revenue is actually earned as a result of these expenses.
5. Full disclosure principle: Require businesses ti disclose sufficient information to the users.
Accounting Constraints
==================
Conservatism: A concept to guide accountants to choose between available options. The selected option should minimize the possibility of overstating income or assets of the company.
Materiality: Require businesses to account only for the items that are deemed significant for a given size of operation.
Accounting Equation
=================
Asset = Liabilities + Owner Equity
Financial Statement Components
============================
Income statement: A summary of revenue and expenses for a specific period of time such as month or a year.
Statement of owners's equity: A summary of the changes in the owner's equity as of a specific date.
Balance Sheet: A list of assets, liabilities and owner's equity as of specific date, usually at the close of the last day of the month or a year.
Statement of cash flows: A summary of the cash receipts and cash payments for a specific period of time, such as a month or a year.
Wednesday, May 21, 2014
SAP Material Master – A Practical Guide
Here is another book in my inbox..
i put this in my blog for my easy reference in the future
so if you are interested, please feel free..
======================================================
| ||
Learn from veteran SAP Materials Management (MM) expert Matt Johnson on the fundamentals of SAP Material Master and valuable cost saving tips.
|
Friday, May 16, 2014
reconciling CO-PA to the General Ledger?
| New books in my mailbox.. is you all interested, do go below link!! -kakshida- Does your company struggle with reconciling CO-PA to the General Ledger? Here are three considerations for addressing reconciliation issues:
Interested in more considerations and a complete reconciliation solution?
Read Reconciling SAP CO-PA to the General Ledger and learn how to effectively solve reconciliation issues between CO-PA and FI in SAP ERP so that you can have confidence in the information derived from CO-PA reports Learn more http://www.amazon.com/ |
Thursday, May 15, 2014
lama tak hupdate ye..
lama dah akak tak hupdate blog ye
tapi banyak gak page view, semua gara2 SAP
ramai minat SAP ye
nanti akak post lagi banyak2 pasai SAP ye
tengok la cemana ek..
minggu ni keje shift malam
baru kul 1am nih, dah nantuk dahh
seb baik banyak keje n tiket hari ni
takde la nantuk sangat, lite2 je ok semua..
akak sambung keje2 dulu naaa
daaaaaa..
tapi banyak gak page view, semua gara2 SAP
ramai minat SAP ye
nanti akak post lagi banyak2 pasai SAP ye
tengok la cemana ek..
minggu ni keje shift malam
baru kul 1am nih, dah nantuk dahh
seb baik banyak keje n tiket hari ni
takde la nantuk sangat, lite2 je ok semua..
akak sambung keje2 dulu naaa
daaaaaa..
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)